The Human Soul in Relation to World Evolution
GA 212
3. The True Nature of Memory II
5 May 1922, Dornach
In order to extend our considerations and link on to what was said last week, let us bring to mind some of the things already known to us. When we consider man as he lives between birth and death we see his life divided into sections which can be studied from various aspects. Attention has often been drawn to the alternating states of waking and sleeping and we know that dreaming is a state between these two. Thus, we have three states of consciousness in ordinary life—waking, dreaming and sleeping. Human nature itself can be divided correspondingly. When we trace the content of ordinary consciousness we experience thinking—i.e., forming mental pictures. I have often pointed out that only in this state, or to the extent that we are in this state, are we really awake. Anyone who observes himself without prejudice will acknowledge that feeling presents a much duller state of consciousness than thinking. Feelings surge through the soul and, unlike mental pictures, we cannot relate them so definitely either to something in the external world or to something remembered. And we are conscious, or at least could become conscious, that as soon as we are awake, feelings come and go very much the way dreams come and go in the intermediate state between waking and sleeping. Anyone who has a sense for comparing different states of consciousness must say to himself: Dreams have a pictorial quality; feelings are more like indefinite forces surging within us. But apart from their content, dreams come and go just as feelings come and go. Furthermore, dreams emerge from a general darkness and dullness of consciousness just as feelings emerge and again submerge within a general inner existence.
When we consider the will we find that what takes place within us when we have a will impulse remains as unknown to us as that which we sleep through. The only aspect that is clear in a will impulse is the thought that initiated it. What next comes into consciousness is the movement of our limbs or the event taking place in the external world through our will. But what takes place in the legs when walking or in the arms when we lift them remains as unconscious as that which takes place between falling asleep and waking. So we can say that while we are awake we experience all three conditions of waking, dreaming and sleeping.
However, we shall only arrive at a comprehensive knowledge of man if we use discernment when comparing what is given us, on the one hand, as sleeping, dreaming and waking; and, on the other, as willing, feeling and thinking. Let us consider sleeping man, on the one hand, and, on the other, man engaged in an act of will. The characteristic feature of sleeping man is that the very factor that makes us human—the experience of the I or ego—is absent. This situation is usually described by saying that the I, between falling asleep and waking up, is outside of what is present before us as physical man.
Let us now compare dreaming man with man experiencing feelings. By means of ordinary self-observation you will immediately recognize that dream pictures come before the soul in a, so to speak, neutral fashion. When we dream, either on waking or before falling asleep, we cannot really say that the pictures come before the soul like a tapestry, rather do they surge and weave within the soul. Thus, what then takes place in the soul differs from what occurs when fully awake. When awake we know that we take hold of the pictures which we then have; we grasp them in our inner being. They are not so nebulous and indefinite as dreams.
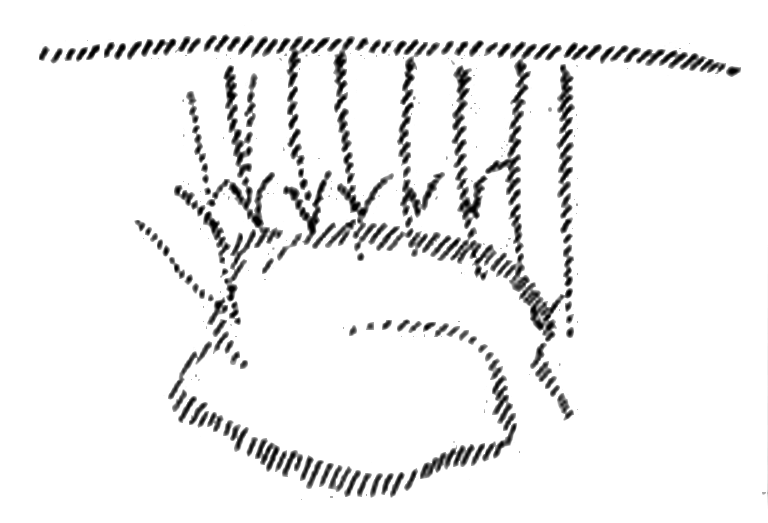
Let me illustrate what has just been described (left hand drawing). Let us imagine man schematically (white lines) and draw what we imagine to be weaving dreams (red lines). One must imagine the red part as a tissue of dreams experienced by the soul which continually withdraws and again approaches the soul.

The moment he wakes up man does not experience such a tissue of weaving pictures. He now has the pictures of whatever he is experiencing firmly within him (right hand drawing). The weaving pictures which were formerly outside are now within him; he lays hold of them with his body and because he does so they are no longer undefined weaving pictures but something which he controls inwardly.
When man is fully awake then what weaves and hovers as dreams become thoughts within him. He is then in control of what now lives in his soul as mental pictures. In this relationship you can see that the soul is taking hold of something which from outside draws into man. What has just been described is in fact the entry of what we call the astral body into man's inner being. To ordinary consciousness it is that which before entry weaves and hovers as dreams. The astral body is, therefore, within us when after waking we begin to think. We then form mental pictures and we know that we do so, for these mental pictures are under our control. As long as they are dreams they hover outside. You need only imagine a kind of cloud that hovers near you in which dreams are weaving. You then draw in this cloud, you now control it from within. Because it is no longer outside you cease to dream. Just as you grasp objects with your hands so do you grasp dreams with your inner being; which means that you have drawn in the astral body.
We must ask: What precisely is it that we now have within us? We can perhaps find a point of reference by looking at certain dreams which are not just pictures but begin also to become indefinite feelings. Just think how often dreams can be quite unpleasant. Many dreams are connected with anxiety. You wake up feeling anxious. In this undefined state of anxiety—less often it may be a state of joy—you have the first glimmer of something which as it further develops becomes fully present as you wake up. What is it that glimmers forth when a dream causes, for example, anxiety?
Such dreams are interwoven with feelings; anxiety is a feeling. The feeling is undefined because the dream is still partly outside the organism; yet it is far enough within to intermingle with feeling. It interweaves with what already lives in the soul as feeling. Only when the astral body has entered completely do you have definite feelings. These are conditioned by the physical organization and can now be penetrated by mental pictures present in the astral body.
When we consider certain nightmares and anxiety dreams in the right light we draw near to what actually takes place when the astral body enters man's physical body. You will always find that it is some disorder in the breathing which causes the state of anxiety of some dreams. From this you can see clearly that the astral body draws in and again draws out through the breath. It is really possible to observe these things if only the observation is thorough enough and free from prejudice. Something can be seen here that enables us to recognize that what weaves in dreams is in fact the astral body and that it draws into our organism by taking hold of the breath as we wake up.
This leads to the recognition of something else that is not normally taken into account but is of great significance. The human being is usually regarded as if he were simply a physical organism, a body built up of solid matter. That is just not true. The least part of the human body is solid, less than ten percent. For the rest it is a water organism, an organism of liquid, so that in reality we must think of this organism built up in such a way that one tenth is solid (see drawing, white lines) and the solid saturated with water (blue lines). You only represent the human organism truly when you see it as a column of liquid in which the solid is deposited.

However, there is more to it. We must also picture the human organism as an organism of air. The air is outside, we breathe it in; a part of the outside air is now within us and we breathe it out again. So we are also an air organism. Let us draw that, too (red lines). It is just this air organism which is taken hold of by the astral body as we wake up. We breathe in the air, it goes through transformations the effect of which pours through the whole organism. The oxygen takes up the carbon and transforms it into carbonic acid. Thus, an air process continually takes place within us.
As we wake up the air process is permeated by the astral body. The movement of the astral body follows the same path as the air through the organism. The air process consists solely of air when we sleep; when we are awake then the movements of the astral body, as it were, swim along within what lives in us as air processes. But now depict to yourselves the following: the astral body draws into that which I have schematically drawn in red and carries out its movements, in fact, carries out its general activity, within the air organism. This all takes place within the watery organism, which is represented in the blue lines. When we are awake, these air processes are in reality processes of the astral body and they continually push against the watery organism. Man's etheric body is within the watery organism both night and day. So you have simultaneously a reciprocal effect between the etheric body and the astral body, as well as between their physical counterparts which are the air processes and the water processes. Thus, you can visualize these processes running their course within man between his breathing and the movements of all the bodily fluids. Yet that is again merely a copy of what takes place between the astral and etheric bodies.
The whole organism consisting of solid, fluid and air is also permeated with warmth (see drawing, yellow lines, page 38). The whole organism has its own warmth—i.e., its own warmth ether. On the gaseous waves moves astrality and in the warmth flowing through the body moves the actual I or ego of man.
So you have the physical body as such, then the fluid body, which is also physical but differentiated from the solid physical body. The fluid physical body has an intimate connection with the etheric body. Then the gaseous organism which has an intimate connection with the astral body, and finally all the warmth processes—that is, the warmth ether in man, which has an intimate connection with the human I. Thus, one can say that in the various physical constituents of man we have a picture of the whole man. The solid part, so to speak, exists by itself; the fluid within the organism cannot exist by itself. Within the head we have very little solid and what there is swims in the cerebral fluid. Within this fluid is the etheric part of the head.
In the breathing process the following takes place: As we breathe in, the breath pushes inwards up through the spinal fluid towards the brain. In our waking state the astral also moves along this thrusting movement towards the etheric part of the head. We have then, on the one hand, an interaction of the movement of the cerebral fluid with the movement of the breath, and, on the other, an interaction of the etheric part of the head—of which what takes place in the cerebral fluid is only an image—with the breathing process, which is again only an image of the astrality in man. We also have a continuous interplay of warmth; the movement of the blood mediates the warmth. On the waves of this sea of warmth our I also moves.
To become clear about these interactions within man's bodily nature it is essential that we represent them vividly to ourselves. Only the solid organism can be observed by itself. The fluid organism does not have the possibility of moving
in waves the way water moves in the external world. The play of movement in the fluid organism is an image of what takes place in the etheric body. Again, what takes place in the delicate processes of breathing is an image of what takes place in man's astral body. Keeping this in mind let us once more look at the cerebral fluid: within it certain movements take place copying movements of the etheric body. Man acquires the etheric body when he descends from spiritual worlds into the physical world. Within the spiritual world he does not yet possess it. But as man takes hold of his physical body he also takes possession of his etheric body; he, as it were, draws out the ether from the cosmos. He can unite with the physical body, which he receives through heredity, only when he has drawn the ether from the cosmos. So that all that lives in the etheric body of man we bring with us when we take hold of the physical body.
The human embryo develops within the maternal body. Let us consider the fluid within the embryo. In general physiology only the solid components, or what appear to be solid components, are examined, not the fluid. Were this to be investigated it would be found that the cerebral fluid, in particular, contains an image of all that which was present already in the ether body, as the ether was drawn together, and which then slips into physical man.

If this is the physical body (see drawing) in which the physical human embryo develops—I do not draw the solid, only the fluid embryo (red lines)—then what as astral and `I' is present descends from the spiritual world; what has been drawn together from the ether slips in (yellow lines). In fact, as he dives down into his physical body the fluid part of the organism absorbs what man brings with him. Therefore, if the movements within the cerebral fluid of the child were to be investigated they would be found to be like a photograph of what the human being had been before he united with the physical body. You see, it is very significant to realize that a photograph is to be found in the cerebral fluid, that is to say in the movements of the cerebral fluid, of what has taken place before conception.
It is fairly easy to understand that a kind of photograph of what existed before conception is to be found in the cerebral fluid. But let us now consider the process of breathing. Breathing appears to be an out and out physical process because of the way our lungs function. Air is drawn in and, under the influence of the external world, the breathing takes place even when we are asleep—that is, even when the eternal part of our being is not united with the temporal part. Our breathing is not affected by whether we are awake or asleep. When we sleep the wave movements of the breath go through the organism; when we are awake they, in addition, carry the astral body. In other words, they are able to carry the astral body but it is not incumbent on them to do so, for when we are asleep they do not.
What follows from this? It follows that the reason the cerebral fluid can carry on by itself is because it is isolated within man's inner being. It constitutes a kind of continuation of what existed before. On the other hand, nothing of what existed before can be continued in this intimate way within our breath. When we consider the human head, we find within the cerebral fluid, that is, within the physical body itself, the actual continuation of pre-natal spiritual man; whereas when we consider the organization of the chest and the process of breathing we find a different situation. The physical breath takes place by itself (see drawing, yellow lines); the spiritual is less strongly connected with the physical process (red lines). Therefore, one must say that in the head, spiritual man, the man of soul and spirit, is closely connected with physical man; they have become a unity. In the chest that is not the case—there the two are more apart; the physical organism is more by itself and so, too, the soul-spiritual.

Let us now compare this with the state of dreaming. When we dream the I and astral body are outside, they are separated from the sleeping body. However, for the chest man, that is to some extent always the case. The chest man—that is, the man of breath and heart, in short, rhythmic man—is the organism for feeling. Feelings run their course like dreams because the soul-spiritual is not so firmly connected with the physical organism, is not so completely within physical man. So you see, if one wants to consider the whole man one must take into account these different interactions of what pertains to the soul and what pertains to the body.
In our materialistic age the human being is considered only in the most external way. This is evident from the way modern science looks upon man as if he were nothing but a solid organism within which the soul is somehow active. On this basis it is impossible to visualize how, for example, an impulse of will, experienced purely within the soul, can lead to the lifting of the arms or legs. In fact, from the point of view of what we experience as the soul's part in an act of will, the human organism, as conceived by modern anatomy and physiology, is like a piece of wood, as alien to the soul as a piece of wood. What in physiology today is described as human legs is like a description of two pieces of wood. They are related to the soul as if they were wooden legs. As little as the soul could have any relationship with two pieces of wood lying about, just as little could it have any relationship with legs as described by modern physiology. However, human legs are penetrated by liquid. Here we already come upon something in which it is easier to understand that the spiritual can be active within it. Yet, it is still difficult.
Once we come to the gaseous, the airy element, then we are in a physical material so fine that it is much easier to visualize the soul element to be within it, and easier still when we come to warmth. Just think how close a connection can come about between the warmth of the physical organism and the soul. You may at some time have had a terrible fright and grown quite hot. There you have an inner experience of the connection between the soul and the warmth in the physical organism. In fact, when we examine the solid, fluid, gaseous and warmth components of the whole organism, we gradually arrive at the soul.
It can be said that the 'I' takes hold of the inner warmth; the astral body of the gaseous; the ether body of the fluid and only the solid remains untouched; in the solid nothing enters. Picture to yourselves the way the human organism functions: You have the human brain (see drawing, page 46) that has fluid in it and also solid parts into which, as I said, the soul does not enter. The solid parts are, in reality, salt deposits; whatever solid we have within us is always salt-like deposit. Our bones consist solely of such deposits. In the brain very fine deposits continually occur and again dissolve. There is always a tendency in our brain to bone formation. The brain has a tendency to become quite bony. But it does not become bony because everything is in movement and is continually dissolved. When we examine the organism, especially the brain, we first find within it a condition of warmth, and within the warmth the air which is the bearer of the astral body and is continually playing into the cerebral fluid while being breathed in and out. We then have the cerebral fluid in which the ether body lives. Then we come to the solid into which the soul cannot enter because it consists of deposited salt. Because of this salt formation, which is less than ten percent of the total organism, we have within us something into which the soul cannot enter.
As human beings we have an organism; within this organism there are warmth, gaseous and fluid elements, all of which the soul can penetrate. But there is something which the soul cannot penetrate. This is comparable to having objects on which light falls but cannot penetrate and is therefore thrown back. Let us say we have a mirror; light cannot go through it and is therefore reflected. Similarly, the soul cannot penetrate the solid salt organism and is, therefore, continually reflected.
If this were not the case, there would be no consciousness at all. Your consciousness consists of soul experiences reflected from the salt organism. You are not aware of the soul life as it is absorbed by the warmth, gaseous and fluid organism; you experience it only because the soul life within the warmth, gaseous and fluid, is reflected everywhere by salt, just as sunbeams are reflected by a mirror. The outcome of this reflection is our mental pictures.

When someone deposits too much salt—salt always takes on forms—then he produces a lot of mental pictures; he becomes rich in thoughts. If too little salt is secreted the thoughts have vague outlines, like reflections from a faulty mirror. Or, said differently, when too much salt is secreted thoughts predominate and become very precise, and he who has them becomes pedantic. He is convinced of the rightness of his thoughts because they arise from so much solid, he becomes materialistic. When too little salt is secreted, or perhaps too much in the rest of the organism but too little in the head, then the thoughts become indefinite and the person becomes fanciful or perhaps he becomes a mystic. Our soul life is dependent on the material processes taking place within us.
It may be necessary, when someone is too prone to fanciful ideas, to administer some remedy that will enable him to deposit more salt or else give better form to the salt he does deposit. He will then escape from his fantasies. However, one should not make too great an effort to cure a human being by physical means of his fantasies or pedantry; not much can be done anyway. To do something different is more important and can be of great value—someone who knows how to observe human beings in regard to both soul and body will notice if there is too much sediment, whether in the head, or in the organs of the rhythmic or metabolic systems. He will notice it because the whole thought configuration becomes different. The manner in which a person alters his thoughts can contribute significantly to a diagnosis. But such delicate reactions are not often noticed. For example, someone may suddenly make mistakes repeatedly when speaking. He does not normally do so, but suddenly he makes mistakes again and again. It may last a few days and then cease. He has suffered a slight ailment, and the mistakes in speaking are merely a symptom. Such instances can often be described quite exactly.
For example, someone may for a few days secrete too much gastric acid. Now what occurs? This gastric acid dissolves certain substances in the stomach, which ought to pass on beyond the stomach. This means that the organism is deprived of these substances with the result that the person's inner mirror pictures lack the necessary sharpness. His thoughts become vague and he makes mistakes in speaking. You will have realized what must be done: One must provide a remedy that will ensure less acidity in the stomach, then the person's thoughts will again become ordered. His digestion is now in order and he ceases to make mistakes when speaking.
Or take the example of someone who absorbs gastric acid too intensely. This can occur if the spleen is abnormally active. When this happens the gastric acid is distributed throughout the body; the body, as it were, becomes all stomach. Such acid sediments are, in fact, the cause of many illnesses. A specific pricking pain may be felt or, if the head is affected, a feeling of dullness. When you look at such a person with insight it will often be found that the absorption of all the acidity has created in him a certain greediness. When someone is permeated with acidity his eyes may lose their friendly expression. If someone is suffering from too much acidity his eyes will reveal it. It is sometimes possible to restore his friendly expression by administering an acid that can be digested in the stomach because it is of a kind that has no tendency to spread throughout the organism.
The reason I am saying all this is to show you that the science of the spirit meant here does not simply contemplate the human soul in a nebulous way. It recognizes the soul as the ruler and builder of the body, active within it everywhere.
The human organism is described nowadays as if it were solid through and through; the solid alone is taken into account. It is impossible to arrive at any conception of how the soul actually exists within the body unless one also considers the fluid, gaseous and warmth elements of the organism. The soul does not live in the solid part of the organism; it does not enter the solid any more than light penetrates a mirror. Light is thrown back from the mirror, the soul retreats everywhere from the salt.
The peculiarity of the soul is that it is deflected from the bones (see drawing, red lines). We carry our bones within us empty of soul. The soul is not within them but is rayed back into the organism.
The bones in the skull are really ingeniously arranged. The soul rays out in all directions and is reflected into our inner being. We do exist within the skull bones but only as solid physical man. If we would make a comprehensive sketch of the head we would have to depict the soul as raying out within the head (see drawing, red lines). If nothing else happened, we would be in a dull unconscious condition. However, as the soul cannot enter the bones of the skull it is rayed back into our inner being (arrows, short red lines).

We experience the soul only when it is reflected into our inner being. So, you see how matters stand: The reality is that you have the soul within you rayed back from the mirror of the skull bones.
Spiritual science does not exclude what is material; on the contrary, recognition of how the soul controls matter makes it, at last, comprehensible. After all one does not come to know that someone is a baker by the fact that he makes certain movements, but from knowing that the movements he makes shape the rolls and croissants. Neither does one come to know the soul through abstract considerations but by knowing that a reflection of the soul's activity is to be found in the physical organism. It is a question of understanding the organism rightly and recognizing that it is an image of the soul. If we cannot make the effort to understand even man's physical nature we shall never learn to know the soul. We must have the goodwill to understand how human nature comes to expression through the physical. What is usually spoken of as soul, by those who will not approach the physical with spiritual insight, is something utterly unreal. It is as unreal as if you had a tasty meal before you and, instead of eating it, tried to eat its reflection in a mirror standing beside it. One can become knowledgeable about the soul only by observing her creative activity and not by persisting to regard it as a mere abstraction. And one should certainly not adopt the view that to be a conscientious spiritual scientist one must scorn the material. Rather should the material be understood spiritually; it will then reveal itself as spirit through and through. To do otherwise is to live in intellectual abstractions, and they obscure rather than enlighten.

